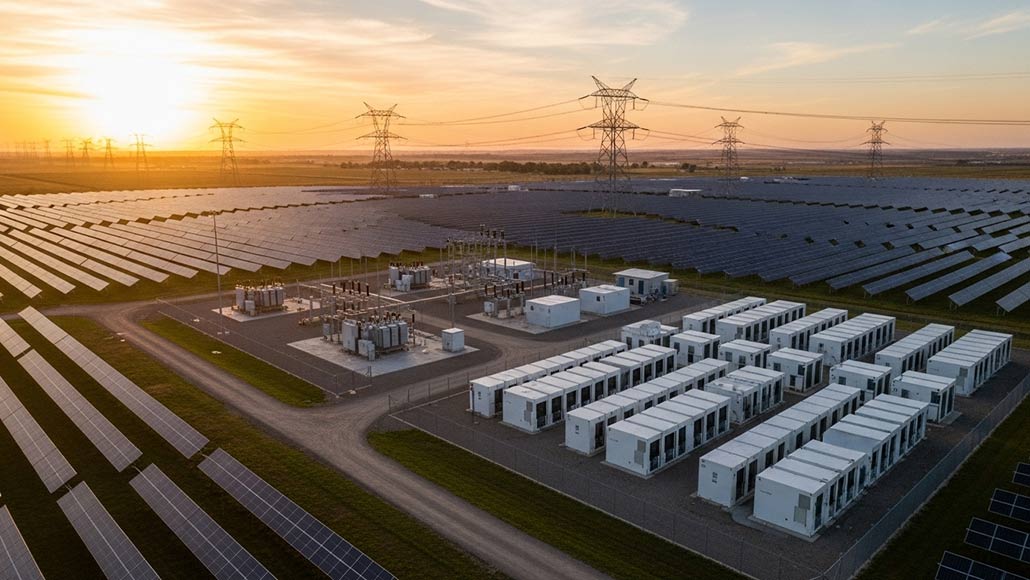
As the worldwide energy shift speeds up, renewable power sources, especially wind as well as solar, are taking center stage. However, their intermittent nature still poses a significant challenge in ensuring that great reliability is there. The rise of grid-scale battery deployment strategies has gone on to become a very crucial element in balancing supply and demand within renewable-dominant power systems. These strategies are not just about storage, but they also involve rethinking the grid architecture, integrating the trading opportunities, optimizing the dispatch, and also enabling real-time agility.
In the years that have gone by, advancement within lithium-ion, hybrid storage technologies, and flow batteries has opened new possibilities when it comes to scaling renewable integration without compromising on the balance. Energy storage is no longer viewed as a peripheral asset, but it is now the central infrastructure component within the clean energy value chain. As countries look forward to attaining 100% renewable energy objectives, strategic battery rollout is going to define the efficiency, the speed, and even the cost-effectiveness when it comes to this shift.
From a B2B standpoint, grid-scale batteries also go on to create novel revenue streams for traders, utilities, and even grid operators by way of unlocking the arbitrary opportunities within the wholesale markets. Energy companies that position themselves early within this evolution of technology are all set to gain both in terms of competitive market advantage as well as operational resilience.
Infrastructure integration along with strategic siting
It is well to be noted that one of the most critical aspects of rolling out grid-scale batteries happens to lie in site selection as well as integration with the present grid infrastructure. Batteries have to be strategically located nearby renewable generation sites in order to absorb excess output during the periods of peak production and also near the demand centers so as to discharge power when there is a spike in consumption.
Apparently, in countries like the US and Australia, battery installations are increasingly located with large-scale solar farms, thereby reducing the transmission losses and elevating the speed of dispatch. This kind of trend is also shaping the procurement strategies since developers go on to prioritize those sites that align with both renewable generation patterns and the congestion points of the grid.
For instance, the energy storage roadmap in California goes on to outline projects that are strategically placed so as to relieve any kind of bottlenecks when it comes to higher renewable zones. Whereas when we talk of Europe, the UK’s national grid is investing in battery projects near the offshore wind connection points in order to stabilize the frequency in real time. Such kind of infrastructure integration makes sure that storage is not a passive asset, but it becomes an active ingredient as far as the grid participation is concerned.
Optimizing the dispatch by way of AI as well as IoT
Modern grid-scale batteries are getting increasingly powered because of artificial intelligence and Internet of Things control systems that enable predictive dispatching, performance monitoring in real time, and a fast response to certain market signals.
Energy management systems, which are AI-driven, can predict demand curves, wholesale market prices, and even the weather patterns so as to determine optimal times when it comes to charging as well as discharging. For grid operators, this goes on to mean fewer cuts in renewable generation and better market participation by way of ancillary services like frequency regulation, as well as voltage support.
Apparently, in South Korea, advanced AI-enabled dispatch systems are already rolled out in order to operate the largest energy storage facility in the country. This will improve both profitability and dependability. These kinds of capabilities also help With trading optimization, thereby enabling the operators to sell the stored energy during high-price periods and also buy during low-price intervals, thereby enhancing the efficiency when it comes to the overall market.
Trading along with market participation
From the viewpoint of supply chain as well as trading, grid-scale batteries are creating a completely new market dynamic. Energy storage assets can now be a part of day-ahead and real-time wholesale markets by offering capacity but also fast response when it comes to grid services.
In the US, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission and its order 841 mandate that energy storage should be allowed to participate within wholesale markets along with traditional generators. This opens certain profitable opportunities when it comes to trading companies so as to leverage the storage as an agile market tool. In a similar way, the market reform plans in Europe emphasize integration of storage into capacity markets as well as ancillary service pools.
This trading potential is especially very relevant when it comes to renewable-dominant systems in which price volatility is pretty high. Batteries can go ahead and absorb surplus power when wind or solar peaks drive the costs down and then discharge during the low generation period when the prices go up. Such kinds of energy arbitrage models are becoming a major driver in investment decisions when it comes to storage infrastructure.
Technology Diversification and Expenditure Trend
It is well to be noted that lithium-ion batteries at present dominate the grid-scale segment because of their declining costs and performance, which is proven. But technology diversification is critical when it comes to meeting varied durations as well as performance requirements of renewable grids. Flow batteries, for instance, offer a longer duration storage of almost 12 hours, making them perfect for smoothing out any kind of daily renewable fluctuations. Hybrid storage systems, which combine rapid-response lithium-ion along with long-duration flow or thermal storage, are also becoming quite a viable model.
Interestingly, cost trajectories remain quite encouraging, with BloombergNEF anticipating further price dips of almost 15 to 20% in the next five years, which are going to be driven by manufacturing scale, maturity in supply chains, and also innovations in recycling. The competitive spectrum is increasingly rewarding for players who embrace multi-technology strategies so as to serve the varied requirements of grids.
Alignment in terms of policy and regulation
It is well to be noted that government policies happen to remain a decisive factor when it comes to speeding up the grid-scale battery rollout. Incentives like the investment tax credit by the US Inflation Reduction Act, when it comes to standalone storage, as well as the renewable integration grants by the EU, have prominently decreased the barriers to investment.
But the regulatory clarity that surrounds the role of storage and capacity planning, access to market, and revenue stacking still remains quite uneven through jurisdictions. Nations that streamline permitting, standardize the process of interconnection, and also integrate storage along with long-term planning are going to be better positioned so as to scale the renewable dominance without risking the stability.
In Japan, for instance, regulatory reforms have already led to growth when it comes to corporate storage rollout. While in India, they are already finalizing its national energy storage mission so as to sync utility procurement with the targets of renewable expansion.
The Long-Term Perspective
It is worth noting that the next decade is going to see grid-scale battery rollout strategies evolve right from pilot projects to the Centre of Infrastructure planning. As renewable penetration grows to more than 50% in many markets, the operational as well as commercial role of storage is only going to rise.
So what are the kinds of trends one must watch out for?
- Expansion within hybrid renewable storage projects in order to lessen the curtailment.
- Integration when it comes to distributed storage fleet, so as to have aggregated grid services.
- Growing participation In platforms pertaining to carbon-neutral power trading.
- Second-life EV battery adoption in applications related to stationary grids.
Interestingly, for investors and utilities, as well as trading houses, the barrier is going to be balancing the near-term returns from arbitrage and grid services with having long-term strategic value in terms of storage within the decarbonization power system.
In the end
Grid-scale battery rollout strategies are no longer just an optional supplement when it comes to renewable energy, but they are an operational requirement and market enabler. By way of strategically siting the assets, making utmost use of AI-driven optimization, and also participating in energy markets as well as diversifying technologies, the dominant renewable grids of the future can attain profitability as well as resilience.
When we talk about it from a B2B perspective, the rapid evolution of the sector is opening certain new trade flows, thereby creating competitive benefits for those who move in early and also redefine the very structure of electricity markets. As the storage technology scales and expenditures fall, its role when it comes to transforming the renewable potential into trade and reliable energy is going to further deepen.